Be careful what you wish for
There is a great desire to achieve super intelligence in machines but it is inefficient, unnecessary and driven mainly by ego. AI already has the ability to generate the necessary driving matrix to produce the required answer with agents to fulfil our requirements for next era problem solving.
With the rise of AI, our collective ability to discern who is a human online and who isn’t is about to become much worse. As a founder and the CEO of OpenAI, Sam Altman bears responsibility for problems like this. Worldcoin, then, serves as his potential solution: a way to definitively distinguish between humans and AIs. If all humans online could prove that they were, in fact, humans, then scams and imposters would dramatically decrease, and the digital landscapes would become more accurate representations of us as a society.
So in order to prove that humans are humans, Worldcoin scans irises, which are unique to their owners. Once Worldcoin has received a unique iris scan, the project issues a digital identity called a World ID. The ID is not a user’s biometric data itself, but an identifier created using a cryptography method called zero-knowledge proofs.
Multi-agents
Agents in artificial intelligence may operate in different environments to accomplish unique purposes. However, all functional agents share these components.
ARCHITECTURE
Architecture is the base the agent operates from. The architecture can be a physical structure, a software program, or a combination. For example, a robotic AI agent consists of actuators, sensors, motors, and robotic arms. Meanwhile, an architecture that hosts an AI software agent may use a text prompt, API, and databases to enable autonomous operations./p>
AGENT FUNCTION
Specialization of the two cerebral hemispheres for related, but different functions became pronounced, and language and other impressive cognitive abilities emerged. The emergence of the granular area of the PFC allowed simians to model their own thoughts. This led to the ability to form future scenarious and outlooks - imagination. This was the slowest of mental skills but was the most far reaching. This led to such things like long term planning and Machavellian plots. The human capacity for this outshone all other life forms.
AGENT PROGRAMME
An agent program is the implementation of the agent function. It involves developing, training, and deploying the AI agent on the designated architecture. The agent program aligns the agent’s business logic, technical requirements, and performance elements.
TYPES OF AGENTS*
SIMPLE REFLEX AGENTS
A simple reflex agent operates strictly based on predefined rules and its immediate data. It will not respond to situations beyond a given event condition action rule. Hence, these agents are suitable for simple tasks that don’t require extensive training. For example, you can use a simple reflex agent to reset passwords by detecting specific keywords in a user’s conversation.
MODEL BASED REFLEX AGENT
A model-based agent is similar to simple reflex agents, except the former has a more advanced decision-making mechanism. Rather than merely following a specific rule, a model-based agent evaluates probable outcomes and consequences before deciding. Using supporting data, it builds an internal model of the world it perceives and uses that to support its decisions.
GOAL BASED AGENTS
Goal-based agents, or rule-based agents, are AI agents with more robust reasoning capabilities. Besides evaluating the environment data, the agent compares different approaches to help it achieve the desired outcome. Goal-based agents always choose the most efficient path. They are suitable for performing complex tasks, such as natural language processing (NLP) and robotics applications.
UTILITY BASED AGENTS
A model-based agent is similar to simple reflex agents, except the former has a more advanced decision-making mechanism. Rather than merely following a specific rule, a model-based agent evaluates probable outcomes and consequences before deciding. Using supporting data, it builds an internal model of the world it perceives and uses that to support its decisions.
LEARNING AGENTS
Learning agents A learning agent continuously learns from previous experiences to improve its results. Using sensory input and feedback mechanisms, the agent adapts its learning element over time to meet specific standards. On top of that, it uses a problem generator to design new tasks to train itself from collected data and past results.
HIERARCHIAL AGENTS
Hierarchical agents are an organized group of intelligent agents arranged in tiers. The higher-level agents deconstruct complex tasks into smaller ones and assign them to lower-level agents. Each agent runs independently and submits a progress report to its supervising agent. The higher-level agent collects the results and coordinates subordinate agents to ensure they collectively achieve goals.
AI-powered virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have become integral to everyday life. These agents perform a range of tasks such as setting reminders, playing music, and providing information, all through voice commands. They are gradually being replaced with newer technologies based on the new generation of large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4o and Google Gemini, and this upgrade will significantly improve their agent capabilities. Virtual assistants learn from user interactions to offer more personalized services. By analyzing usage patterns, they refine their responses and recommendations over time. This continuous learning allows them to cater to individual preferences, enhancing their utility and making them useful tools for managing daily activities.
Agent Applications
Virtual Assistants
Customer Service
AI agents revolutionize customer service by providing instant responses to queries through chatbots and virtual assistants. These AI-powered tools handle a wide array of customer interactions, from answering common questions to processing orders, significantly reducing wait times and improving service efficiency. AI agents in customer service can analyze customer interactions to identify patterns and preferences. This data-driven approach allows businesses to personalize services and improve customer satisfaction.
Healthcare
AI agents in healthcare assist with diagnostics, treatment recommendations, and patient care management. They analyze medical records, research data, and patient histories to provide accurate and timely diagnoses. These agents support doctors by offering evidence-based treatment options and predicting patient outcomes. Beyond clinical settings, AI agents streamline administrative tasks in healthcare institutions. They manage schedules, handle billing, and ensure regulatory compliance, reducing administrative burdens and operational costs. Their ability to enhance clinical decision-making and operational efficiency underscores the transformative potential of AI in healthcare.
Autonomous Machines
In autonomous vehicles, AI agents manage navigation, obstacle detection, and traffic rule compliance. They process data from sensors and cameras in real-time to make driving decisions, ensuring safe and efficient travels. These AI systems continuously learn and adapt to various driving conditions, improving their reliability and performance over time. Additionally, AI agents in autonomous vehicles contribute to advancements in traffic management by communicating with other vehicles and infrastructure. This collective intelligence can optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. Also drones and other airbourne vehicles.
The list goes on ...
THE LOCAL AGENTS MAY IMPROVE & DECONCENTRATE RESOURCE USUAGE
Although corporations might wish to keep their agents in-house and proprietorial, it may be more efficient and cheaper to share them and improve them with joint input. The smaller companies have proved themselves very agile and efficient at producing smaller agents/tools than the behemoths. This would also allow agents to be nearer more favourable areas with resources not plundered like their larger brethren. This would encourage local AI centres to flourish.
Small Language Models
With more directed and verified data smaller models, both LLMS and LQMS can use smaller compute power to answer more verified and targeted information. The two models may even be amalgamated to produce a larger spectrum output to incorporate the best answers for cross discipline questions.
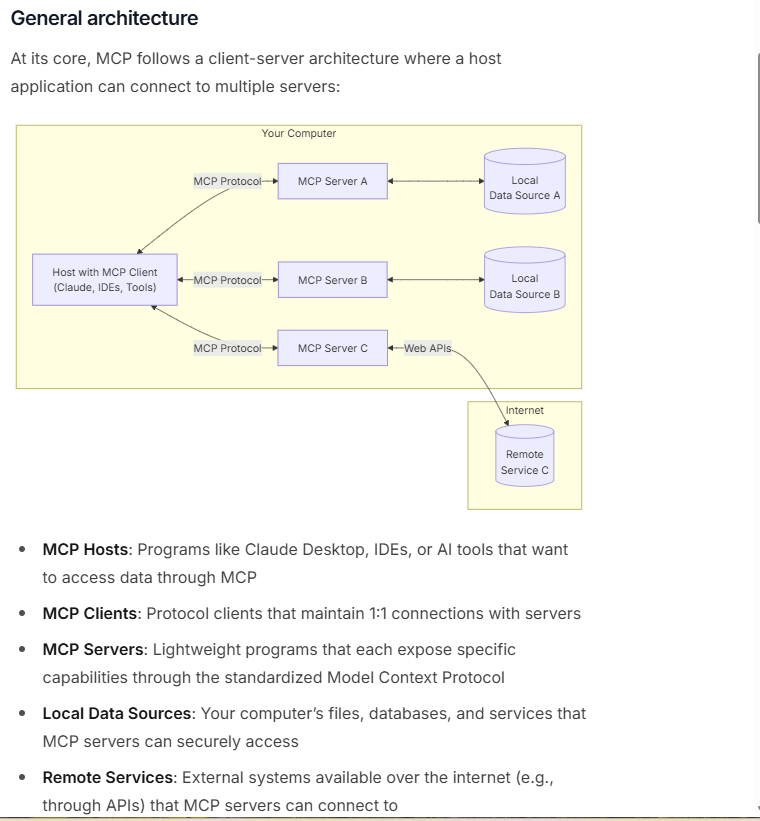
Model Context Protocol